What is low-carb diet?
A low-carb diet has become more popular these days. The idea is to switch your body to burn fat as fuel instead of relying on carbohydrates as fuel.
A low-carb diet is simply by;
- minimizing your intake of high-carb foods like – sugary foods, rice, noodles, bread, potatoes, sugary drinks, and high-sugar junk foods.
- Incorporate higher in dietary fat (with sufficient amounts of protein) e.g; meat, fish, eggs, vegetables growing above ground and natural fats (like butter).
All you need to do is to eat whole foods that create complete, nutritious, and also satisfying meals.(7, 8, 9)
Here are 7 other popular ways to go for a low carb:
- A low-carb, high-fat diet plan (LCHF) or
- A keto diet plan.
- Low-Carb Paleo Diet
- The Atkins Diet
- Eco-Atkins
- Zero-Carb
- Low-Carb Mediterranean Diet
Why low-carb diet?
Scientific studies show that compared to other diets, low carb is generally more effective for weight loss and numerous health markers.(1,2,3,4,5,6) These diets have become commonly used for years and also are endorsed by many doctors for patients with insulin-resistance such as for obesity and diabetes. Plus, there’s no need to count calories.
For decades fat has been victimized and labeled as harmful to our health. If you noticed, commercially labeled ‘low-fat’ products, often full of sugar, have emerged on supermarket shelves.
Since the start of the Low-fat diet campaign in around 1970s has possibly corresponded with the start of the obesity epidemic. While this doesn’t prove causation, it’s clear the low-fat message didn’t prevent the obesity increase, and it is possible it contributed.
When you avoid sugar and starches, your blood sugar tends to become more stable and the levels of insulin (a fat-storing hormone) will start reducing and become more stable too.(10)
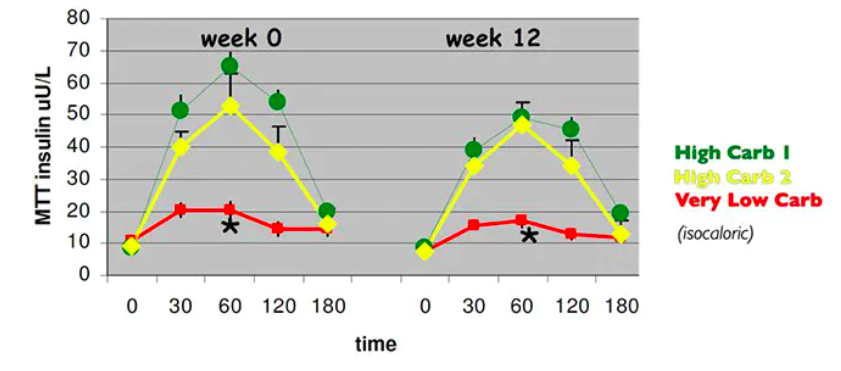
Figure from Boden et al

Figure from Hernandez et al.
In longer trials, low-carb diets have also been demonstrated for fasting insulin levels, in longer RCTs like these: NEJM 2003, Lipids 2009.
This helps enhance fat burning as fuel and may make you feel more satiated, thereby naturally reducing food intake frequency and favoring weight loss.